
by barqar | May 15, 2025 | Cataracts, Eye Health, Uncategorized
Diabetes affects more than just your blood sugar. It can also have a serious impact on your vision. Over time, high blood glucose levels can damage the small blood vessels in the eyes, leading to a group of conditions known as diabetic eye disease. These conditions...
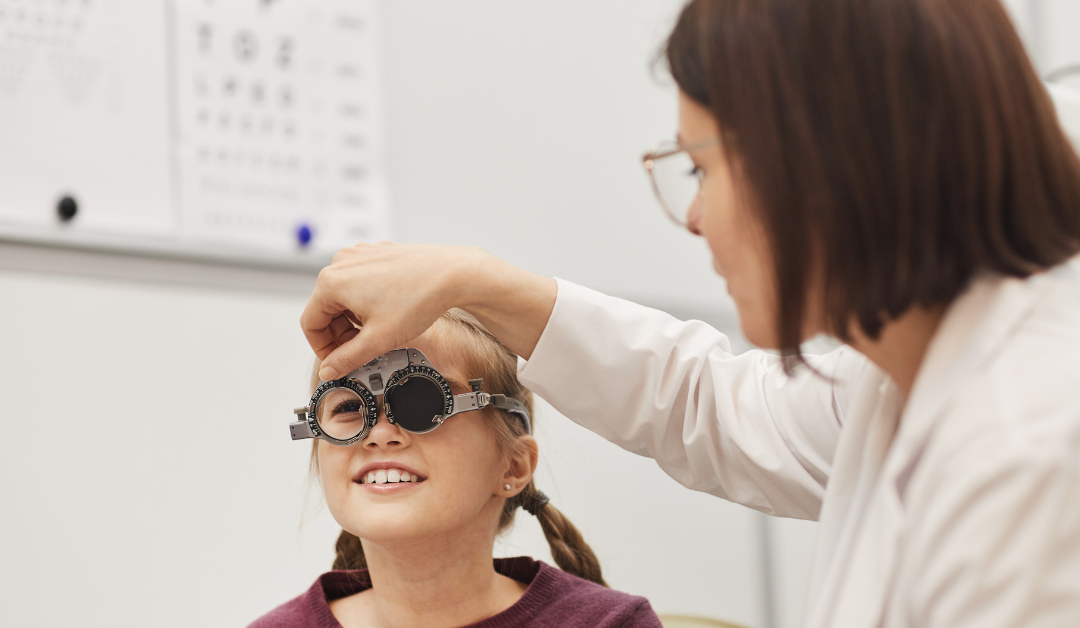
by barqar | Jan 15, 2025 | Eye Health, News Articles, Pediatric Ophthalmology
As a parent, you want to give your child every opportunity to succeed—and pediatric eye health plays a vital role in their development. From learning in the classroom to playing with friends, clear eyesight is essential for a child’s academic, social, and physical...

by ecvaeyeadminz | Sep 18, 2024 | Eye Health
Our eyes are our windows to the world, yet with so much conflicting information out there, it’s easy to feel uncertain about what truly affects their health. From the impact of screen time to the necessity of regular check-ups, understanding how to care for your...

by ecvaeyeadminz | Sep 7, 2024 | Eye Health
Drooping eyelids, or ptosis, can significantly impact both appearance and vision, leading to a range of issues from aesthetic concerns to more serious functional impairments. For those struggling with this condition, it’s not just about how you look in the...

by preichert | Aug 21, 2024 | Eye Health
The impact of drooping eyelids is often far more significant than people expect. When the eyelids droop, it makes it difficult to see clearly or keep the eyes open. This condition, known as ptosis, can substantially affect daily life, affecting everything from reading...

by preichert | Aug 8, 2024 | Eye Health
Lazy eye, or amblyopia, often goes unnoticed until it begins to affect daily activities. Imagine seeing the world through a lens that is always slightly out of focus in one eye while the other works perfectly. This condition can impact both children and adults,...







